All the functions and senses of our body are controlled by the central nervous system - CNS.
This system consist of the brain, spinal cord, and a chain of peripheral nerves that spread throughout the body from the spinal cord.
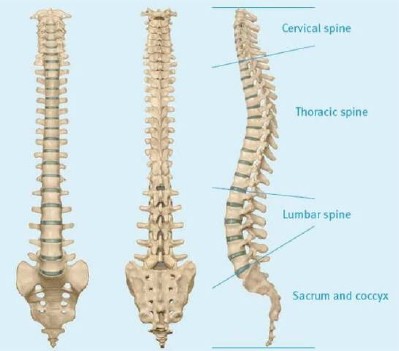
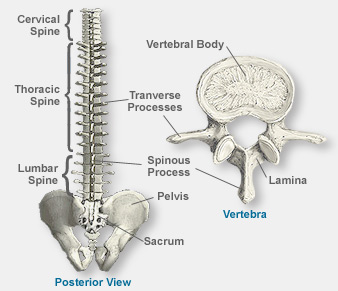
The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain, to inside the bones of the backbone, known as the spine or the spinal column. The spinal cord does not extend the full length of the spinal column, but ends in the small of the back (the lumbar area). The spinal cord is surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid - CSF and by several layers of protective structures called meninges. Meninges are made up of three different layers: dura mater (outer layer), arachnoid mater (middle) and pia mater (inner). The dura mater is the strongest outermost layer. The backbone is made up of bones called vertebrae. The nerves spread out from the spinal cord, between the vertebrae. At each vertebral level of the spine there are a pair of nerve roots. These nerves go to supply particular parts of our body.
Healthy children
means
healthy adults
Non surgical intensive physiotherapeutic treatment for scoliosis of the spine
Joanna Slup
london physiotherapist exercise scoliosis
lateral spine sclerosis:
S C O L I O S I S I N L O N D O N
Spine Scoliosis Centre